When it comes to managing your money effectively, two terms often come up: financial planning vs. budgeting. While they are closely related, they serve different purposes in achieving financial stability and success. Understanding the distinction between financial planning vs. budgeting is crucial for creating a comprehensive strategy for your financial future.
Table of Contents
What is Financial Planning?
Financial planning is a long-term, holistic approach to managing your finances. It encompasses setting financial goals, creating strategies to achieve them, and periodically reviewing your progress. Financial planning addresses various aspects of your financial life, including saving, investing, retirement, insurance, and estate planning.
Key Elements of Financial Planning:
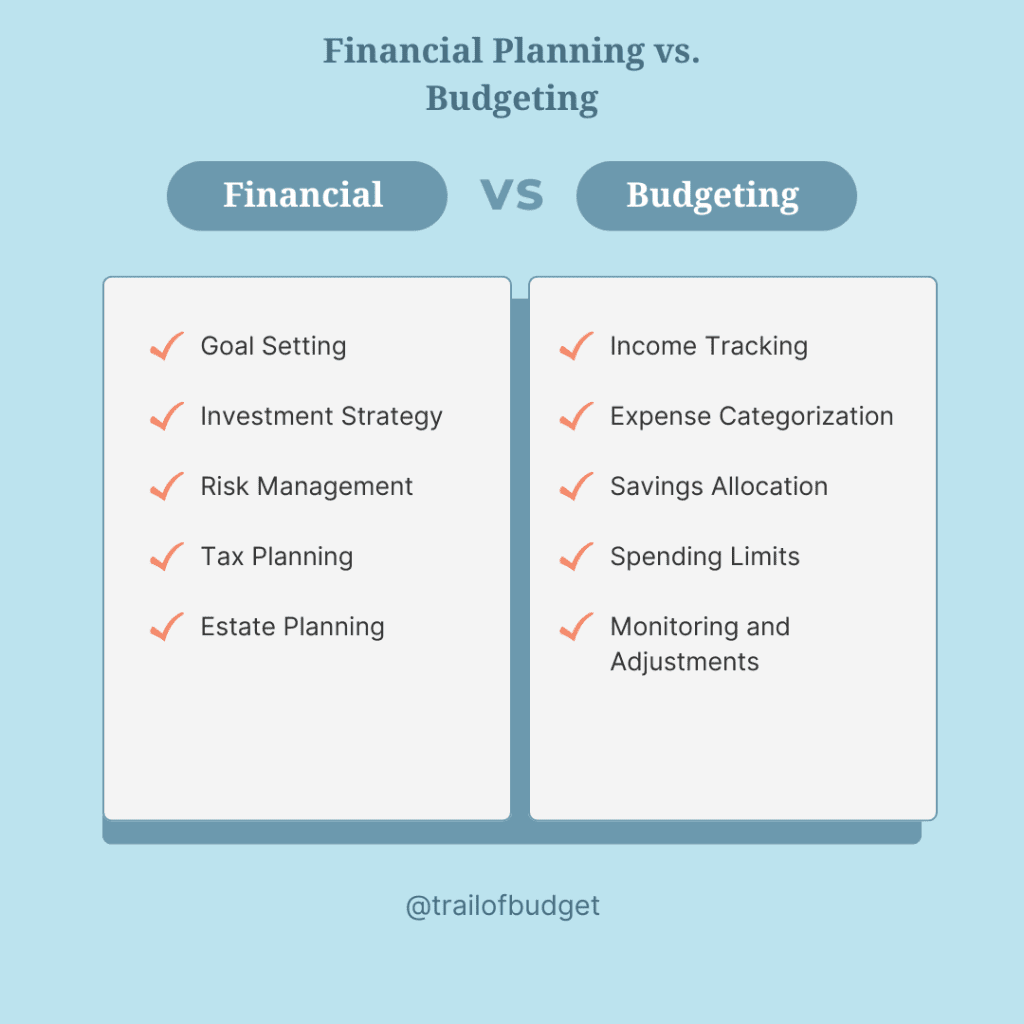
- Goal Setting: Define short-term, medium-term, and long-term financial objectives, such as buying a home, saving for a child’s education, or retiring comfortably.
- Investment Strategy: Identify the best investment vehicles to grow your wealth, based on your risk tolerance and time horizon.
- Risk Management: Ensure adequate insurance coverage to protect against unforeseen events.
- Tax Planning: Minimize tax liabilities through strategic investments and deductions.
- Estate Planning: Plan for wealth transfer and legacy-building.
Benefits of Financial Planning:
- Provides a clear roadmap for your financial future.
- Helps prioritize spending and saving.
- Encourages disciplined financial behavior.
- Offers peace of mind through risk mitigation.
What is Budgeting?
Budgeting, on the other hand, is a short-term tool for managing your income and expenses. It involves creating a plan to allocate your income to cover essential expenses, discretionary spending, and savings goals. Budgeting ensures you live within your means and avoid unnecessary debt.
Key Elements of Budgeting:
- Income Tracking: Understand how much money you earn from all sources.
- Expense Categorization: Identify fixed expenses (e.g., rent, utilities) and variable expenses (e.g., dining out, entertainment).
- Savings Allocation: Set aside a portion of your income for emergency funds, retirement, or other savings goals.
- Spending Limits: Establish spending caps for discretionary categories.
- Monitoring and Adjustments: Regularly review your budget to ensure it aligns with your financial situation.
Benefits of Budgeting:
- Prevents overspending and promotes financial discipline.
- Helps build an emergency fund.
- Identifies opportunities to cut unnecessary expenses.
- Supports short-term financial goals.
Financial Planning vs. Budgeting: Key Differences
| Aspect | Financial Planning | Budgeting |
| Time Frame | Long-term (years to decades) | Short-term (monthly or yearly) |
| Focus | Big-picture financial goals | Day-to-day income and expense management |
| Components | Investments, retirement, taxes, insurance | Income, fixed and variable expenses, savings |
| Flexibility | Adjusted periodically | Requires frequent adjustments |
| Outcome | Wealth creation and financial security | Financial stability and expense control |
How Financial Planning vs. Budgeting Work Together
While financial planning vs. budgeting are distinct, they are complementary. Budgeting lays the foundation for financial planning by ensuring you have the resources to achieve your goals. Conversely, financial planning provides the vision and direction for how to allocate your budget effectively.
Example:
Imagine you’re saving for a down payment on a house. Your financial plan outlines the amount you need, the timeline, and the investment strategy to grow your savings. Your budget, meanwhile, ensures you set aside a specific amount each month while covering your other expenses.
Tips for Effective Financial Management
- Start with a Budget: Track your income and expenses to understand your financial baseline.
- Set Clear Goals: Use financial planning to define what you want to achieve.
- Automate Savings: Simplify budgeting by setting up automatic transfers to savings accounts.
- Review Regularly: Periodically revisit both your budget and financial plan to ensure they remain aligned with your goals and circumstances.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consider consulting a financial advisor to develop a tailored plan.
Conclusion
Mastering the difference between financial planning vs. budgeting is key to taking control of your finances. Budgeting helps you manage your day-to-day spending, while financial planning focuses on long-term goals and strategies. Together, these tools can lead to financial security and success.
Internal Links:
- 8 Steps to Create a Financial Plan That Works
- Financial Planning 101: A Beginner’s Guide to Building Wealth
External Links:

